What Can Cause Heel Discomfort To Appear
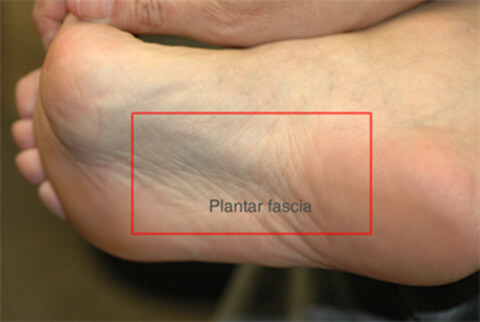
Overview
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot disorder that affects more than two million people every year, especially runners. It is inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue on the bottom of the foot. The most common area of pain is directly on the bottom of the heel, although some people may only have pain in the arch of the foot. Diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is typically done through a physical examination, which includes listening to the patient history, palpation of the heel and possibly x-rays.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis is caused by small, repetitive trauma to the plantar fascia. This trauma can be due to activity that puts extra stress on the foot. Plantar fasciitis is most common in people who are 40-60 years old. Other risk factors that increase your chance of getting plantar fasciitis include physical exertion, especially in sports such as running, Volleyball, tennis, a sudden increase in exercise intensity or duration, physical activity that stresses the plantar fascia. People who spend a lot of time standing, a sudden increase in activities that affect the feet, obesity or weight gain, pre-existing foot problems, including an abnormally tight Achilles tendon, flat feet, or an ankle that rolls inward too much. Poor footwear. Heel spurs.
Symptoms
Symptoms of plantar fasciitis can occur suddenly or gradually. When they occur suddenly, there is usually intense heel pain on taking the first morning steps, known as first-step pain. This heel pain will often subside as you begin to walk around, but it may return in the late afternoon or evening. When symptoms occur gradually, a more long-lasting form of heel pain will cause you to shorten your stride while running or walking. You also may shift your weight toward the front of the foot, away from the heel.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will perform a physical exam to check for tenderness in your foot and the exact location of the pain to make sure that it’s not caused by a different foot problem. The doctor may ask you to flex your foot while he or she pushes on the plantar fascia to see if the pain gets worse as you flex and better as you point your toe. Mild redness or swelling will also be noted. Your doctor will evaluate the strength of your muscles and the health of your nerves by checking your reflexes, your muscle tone, your sense of touch and sight, your coordination, and your balance. X-rays or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan may be ordered to check that nothing else is causing your heel pain, such as a bone fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
If you walk or run a lot, cut back a little. You probably won't need to stop walking or running altogether. If you have either flatfeet or a high arch, ask your doctor about using inserts for your shoes called orthotics. Orthotics are arch supports. You will need to be fitted for them. If you are overweight, losing weight can help lessen your heel pain. If your job involves standing on a hard floor or standing in one spot for long periods, place some type of padding on the floor where you stand.
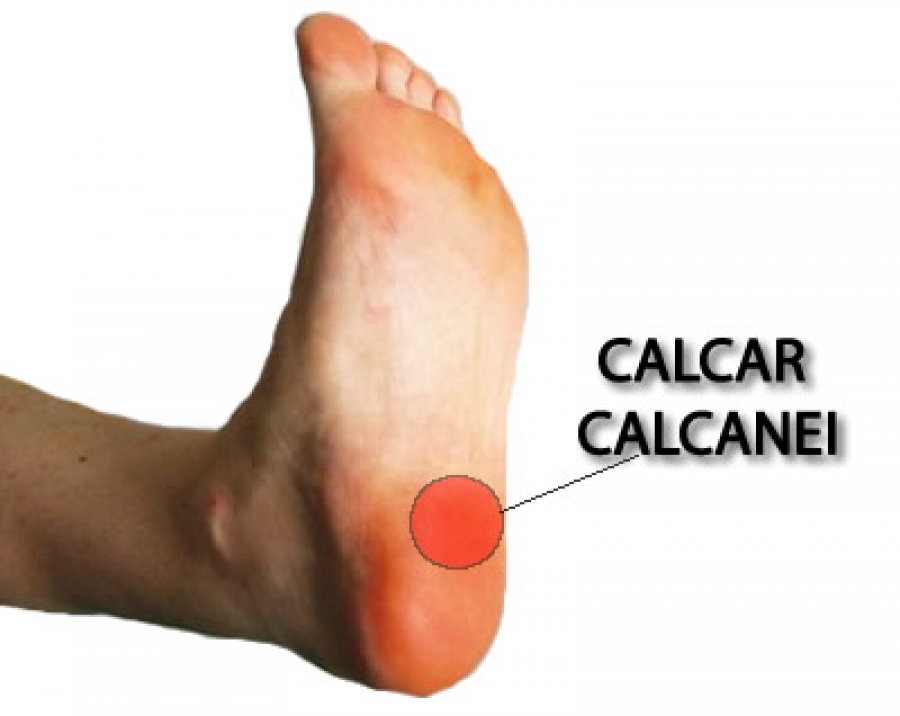
Surgical Treatment
Most studies indicate that 95% of those afflicted with plantar fasciitis are able to relieve their heel pain with nonsurgical treatments. If you are one of the few people whose symptoms don't improve with other treatments, your doctor may recommend plantar fascia release surgery. Plantar fascia release involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament in order to release the tension and relieve the inflammation of the ligament. Overall, the success rate of surgical release is 70 to 90 percent in patients with plantar fasciitis. While the success rate is very high following surgery, one should be aware that there is often a prolonged postoperative period of discomfort similar to the discomfort experienced prior to surgery. This pain usually will abate within 2-3 months. One should always be sure to understand all the risks associated with any surgery they are considering.
Stretching Exercises
Exercises designed to stretch both your calf muscles and your plantar fascia (the band of tissue that runs under the sole of your foot) should help relieve pain and improve flexibility in the affected foot. A number of stretching exercises are described below. It's usually recommended that you do the exercises on both legs, even if only one of your heels is affected by pain. This will improve your balance and stability, and help relieve heel pain. Towel stretches. Keep a long towel beside your bed. Before you get out of bed in the morning, loop the towel around your foot and use it to pull your toes towards your body, while keeping your knee straight. Repeat three times on each foot. Wall stretches. Place both hands on a wall at shoulder height, with one of your feet in front of the other. The front foot should be about 30cm (12 inches) away from the wall. With your front knee bent and your back leg straight, lean towards the wall until you feel a tightening in the calf muscles of your back leg. Then relax. Repeat this exercise 10 times before switching legs and repeating the cycle. You should practise wall stretches twice a day. Stair stretches. Stand on a step of your stairs facing upstairs, using your banister for support. Your feet should be slightly apart, with your heels hanging off the back of the step. Lower your heels until you feel a tightening in your calves. Hold this position for about 40 seconds, before raising your heels back to the starting position. Repeat this procedure six times, at least twice a day. Chair stretches. Sit on a chair, with your knees bent at right angles. Turn your feet sideways so your heels are touching and your toes are pointing in opposite directions. Lift the toes of the affected foot upwards, while keeping the heel firmly on the floor. You should feel your calf muscles and Achilles tendon (the band of tissue that connects your heel bone to your calf muscle) tighten. Hold this position for several seconds and then relax. Repeat this procedure 10 times, five to six times a day. Dynamic stretches. While seated, roll the arch of your foot (the curved bottom part of the foot between your toes and heel) over a round object, such as a rolling pin, tennis ball or drinks can. Some people find that using a chilled can from their fridge has the added benefit of helping to relieve pain. Move your foot and ankle in all directions over the object for several minutes. Repeat the exercise twice a day.
What Is Painful Heel And Best Ways To Successfully Treat It

Overview
Do you have sharp, stabbing, and/or aching pain on the bottom of your heel or arch?
Is the pain more severe when you first get up in the morning or when you first start walking after rest? If this describes your pain then you probably suffer from a condition known as PLANTAR FASCIITIS. It sounds complicated, but plantar fasciitis is actually one of the most common foot problems. In the past plantar fasciitis has been called by other names, such as heel spur syndrome, bone spurs or a stone bruise on the heel. The plantar fascia is a long thick ligament that runs along the arch of your foot from your heel bone (the calcaneus) to the ball of the foot. The job of the plantar fascia is to help support your arch. When the fascia becomes inflamed and painful we call this PLANTAR FASCIITIS. The pain from plantar fasciitis most commonly occurs near the attachment of the fascia to the calcaneus (heel bone), which is why most people who suffer from plantar fasciitis have pain on the bottom or inside of the heel. However, the pain can be anywhere along the fascia from the heel to the ball of the foot.
Causes
Because the plantar fascia supports your foot and gets used every time you take a step, it has to absorb a large amount of stress and weight. If too much pressure is put on the plantar fascia, the fibers can become damaged or start to tear. The body responds by causing inflammation in the affected area. This is what causes the pain and stiffness of plantar fasciitis. Things that can increase the risk of plantar fasciitis include tight calf muscles. Tight calves make it harder to flex your foot, and this puts more stress on the plantar fascia. Weight. Carrying a few extra pounds puts added pressure on your feet every time you take a step. Activities that put a lot of stress on the feet. This includes things like running, hiking, dancing, and aerobics. Bad shoes. Footwear that doesn't give your foot the support it needs increases your risk of plantar fasciitis. You'll want to ditch any shoes that have thin soles or inadequate arch support, or ones that don't fit your feet properly. Routinely wearing high heels can also cause your Achilles tendon to contract over time, making it harder to flex your foot. Jobs that involve a lot of standing or walking on hard surfaces. Jobs that keep you on your feet all day, like waiting tables or working in a store, can cause damage to your plantar fascia. High arches, flat feet, or other foot problems. The shape of your foot can affect the way your weight is distributed on your feet when you stand. If weight distribution is a bit off, it can add to a person's risk of plantar fasciitis. How someone walks can increase the stress on certain parts of the foot too.
Symptoms
Heel pain is the most common symptom associated with plantar fasciosis. Your heel pain may be worse in the morning or after you have been sitting or standing for long periods. Pain is most common under your heel bone, but you also may experience pain in your foot arch or on the outside aspect of your foot. Other common signs and symptoms of plantar fasciosis include mild swelling and redness in your affected area, tenderness on the bottom of your heel, impaired ability to ambulate.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will perform a physical exam to check for tenderness in your foot and the exact location of the pain to make sure that it’s not caused by a different foot problem. The doctor may ask you to flex your foot while he or she pushes on the plantar fascia to see if the pain gets worse as you flex and better as you point your toe. Mild redness or swelling will also be noted. Your doctor will evaluate the strength of your muscles and the health of your nerves by checking your reflexes, your muscle tone, your sense of touch and sight, your coordination, and your balance. X-rays or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan may be ordered to check that nothing else is causing your heel pain, such as a bone fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
Night splints are treatment that can help stretch your calf and the arch of your foot. Night splints are a type of brace that holds your foot in a flexed position and lengthens the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon overnight. This can prevent morning pain and stiffness. Special orthotics, or arch supports, for your shoes may help alleviate some of the pain by distributing pressure, and can prevent further damage to the plantar fascia. A boot cast may be used to immobilize your foot and reduce strain while the plantar fascia heals. A boot cast looks like a ski boot and can be removed for bathing.

Surgical Treatment
The most common surgical procedure for plantar fasciitis is plantar fascia release. It involves surgical removal of a part from the plantar fascia ligament which will relieve the inflammation and reduce the tension. Plantar fascia release is either an open surgery or endoscopic surgery (insertion of special surgical instruments through small incisions). While both methods are performed under local anesthesia the open procedure may take more time to recover. Other surgical procedures can be used as well but they are rarely an option. Complications of plantar fasciitis surgery are rare but they are not impossible. All types of plantar fasciitis surgery pose a risk of infection, nerve damage, and anesthesia related complications including systemic toxicity, and persistence or worsening of heel pain.
Treatment For Bunions
The causes of lip swelling could range from trauma and contact dermatitis to allergic reactions to certain medical conditions. I am a 44 year old Pe teacher who has been experiencing Ball Of Foot Pain since October. Vinegar has been used as a condiment for several centuries.
If changing your shoes isn't helping to solve your foot pain, it is time for us to step in. Contact Dr. Jeff Bowman at Houston Foot Specialists for treatment that will keep your feet feeling great. Inserting arch support insoles in the shoes is also a good option.
Those affected by inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and Achilles tendonitis are also likely to experience pain and swelling in the ankles. If the joints in the feet get affected by osteoarthritis, it gives rise to pain, stiffness, swelling in or around the joint, and restricted range of motion. Since pain in the feet could be caused due to a variety of reasons, the treatment will depend on the underlying cause. Many a time, pain could be experienced by people who perform high-impact exercises such as running, jogging and other sports. Those who have been experiencing pain while running must make sure that they wear a good quality footwear. Painkillers or steroids might be prescribed for the treatment of a sprained ankle.
The spur occurs where the plantar fascia attaches, and the pain in that area is really due to the plantar fascia attachment being irritated. However, there are many people with heel spurs who have no symptoms at all. Haglund's deformity is a bony growth on the back of the heel bone, which then irritates the bursa and the skin lying behind the heel bone. Achilles tendinopathy is degeneration of the tendon that connects your calf muscles to your heel bone. Stress fractures are common in military training.
Bunions are bony lumps that develop on the side of your foot and at the base of your big toe. They're the result of a condition called hallux valgus, which causes your big toe joint to bend towards your other toes and become may also develop a bursa here too, especially if your shoes press against the bunion. Sometimes swellings or bursae on the joints in your feet are also called bunions, but these aren't the same as bunions caused by hallux valgus. Hallux valgus is different to hallux rigidus, which is osteoarthritis of the big toe joint. Hallux rigidus causes your big toe to become stiff and its range of movement is reduced. Symptoms of a bunion can be controlled by choosing shoes with a soft, wide upper to reduce pressure and rubbing on your joint. Toes form hammer or claw shape.
If changing your shoes isn't helping to solve your foot pain, it is time for us to step in. Contact Dr. Jeff Bowman at Houston Foot Specialists for treatment that will keep your feet feeling great. Inserting arch support insoles in the shoes is also a good option.
Those affected by inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and Achilles tendonitis are also likely to experience pain and swelling in the ankles. If the joints in the feet get affected by osteoarthritis, it gives rise to pain, stiffness, swelling in or around the joint, and restricted range of motion. Since pain in the feet could be caused due to a variety of reasons, the treatment will depend on the underlying cause. Many a time, pain could be experienced by people who perform high-impact exercises such as running, jogging and other sports. Those who have been experiencing pain while running must make sure that they wear a good quality footwear. Painkillers or steroids might be prescribed for the treatment of a sprained ankle.

The spur occurs where the plantar fascia attaches, and the pain in that area is really due to the plantar fascia attachment being irritated. However, there are many people with heel spurs who have no symptoms at all. Haglund's deformity is a bony growth on the back of the heel bone, which then irritates the bursa and the skin lying behind the heel bone. Achilles tendinopathy is degeneration of the tendon that connects your calf muscles to your heel bone. Stress fractures are common in military training.
Bunions are bony lumps that develop on the side of your foot and at the base of your big toe. They're the result of a condition called hallux valgus, which causes your big toe joint to bend towards your other toes and become may also develop a bursa here too, especially if your shoes press against the bunion. Sometimes swellings or bursae on the joints in your feet are also called bunions, but these aren't the same as bunions caused by hallux valgus. Hallux valgus is different to hallux rigidus, which is osteoarthritis of the big toe joint. Hallux rigidus causes your big toe to become stiff and its range of movement is reduced. Symptoms of a bunion can be controlled by choosing shoes with a soft, wide upper to reduce pressure and rubbing on your joint. Toes form hammer or claw shape.
Achilles Tendonitis The Facts
Overview
 Achilles tendinitis is an irritation/inflammation in the achilles tendon, which attaches to the back of the heel. It is often a result of overuse and occurs frequently in runners who have altered their training suddenly, either with regard to duration or intensity. This injury is also prevalent in middle-aged people who are active.
Achilles tendinitis is an irritation/inflammation in the achilles tendon, which attaches to the back of the heel. It is often a result of overuse and occurs frequently in runners who have altered their training suddenly, either with regard to duration or intensity. This injury is also prevalent in middle-aged people who are active.
Causes
Over-pronation, injury and overstresses of the tendon are some of the most common causes. Risk factors include tight heel cords, poor foot alignment, and recent changes in activities or shoes. During a normal gait cycle, the upper and lower leg rotate in unison (i.e. internally during pronation and externally during supination). However, when a person over-pronates, the lower leg is locked into the foot and therefore continues to rotate internally past the end of the contact phase while the femur begins to rotate externally at the beginning of midstance. The Gastrocnemius muscle is attached to the upper leg and rotates externally while the Soleus muscle is attached to the lower leg and rotates internally during pronation. The resulting counter rotation of the upper and lower leg causes a shearing force to occur in the Achilles tendon. This counter rotation twists the tendon at its weakest area, namely the Achilles tendon itself, and causes the inflammation. Since the tendon is avascular, once inflammation sets in, it tends to be chronic.
Symptoms
People with Achilles tendinitis may experience pain during and after exercising. Running and jumping activities become painful and difficult. Symptoms include stiffness and pain in the back of the ankle when pushing off the ball of the foot. For patients with chronic tendinitis (longer than six weeks), x-rays may reveal calcification (hardening of the tissue) in the tendon. Chronic tendinitis can result in a breakdown of the tendon, or tendinosis, which weakens the tendon and may cause a rupture.
Diagnosis
A doctor examines the patient, checking for pain and swelling along the posterior of the leg. The doctor interviews the patient regarding the onset, history, and description of pain and weakness. The muscles, tissues, bones, and blood vessels may be evaluated with imaging studies, such as X-ray, ultrasound, or MRI.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The initial aim of the treatment in acute cases is to reduce strain on the tendon and reduce inflammation until rehabilitation can begin. This may involve, avoiding or severely limiting activities that may aggravate the condition, such as running or uphill climbs. Using shoe inserts (orthoses) to take pressure off the tendon. Wear supportive shoes. Reducing Inflammation by icing. Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Heel cups and heel lifts can be used temporarily to take pressure off the tendon, but must not be used long term as it can lead to a shortening of the calf. Calf Compression Sleeves. Placing the foot in a cast or restrictive ankle-boot to minimize movement and give the tendon time to heal. This may be recommended in severe cases and used for about eight weeks.

Surgical Treatment
There are three common procedures that doctor preform in order help heal the tendinitis depending on the location of the tendinitis and amount of damage to the tendon, including: Gastrocnemius recession - With this surgery doctors lengthen the calf muscles because the tight muscles increases stress on the Achilles tendon. The procedure is typically done on people who have difficulty flexing their feet even with constant stretching. Debridement and Repair - When there is less than 50% damage in the tendon, it is possible for doctors to remove the injured parts and repair the healthy portions. This surgery is most done for patients who are suffering from bone spurs or arthritis. To repair the tendon doctors may use metal or plastic anchors to help hold the Achilles tendon in place. Patients have to wear a boot or cast for 2 weeks or more, depending and the damage done to the tendon. Debridement with Tendon Transfer - When there is more the 50% damage done to the Achilles tendon, and Achilles tendon transfer is preformed because the remain healthy tissue is not strong enough. The tendon that helps the big toe move is attached to give added strength to the damaged Achilles. After surgery, most patients don?t notice any difference when they walk or run.
Prevention
Stretching of the gastrocnemius (keep knee straight) and soleus (keep knee bent) muscles. Hold each stretch for 30 seconds, relax slowly. Repeat stretches 2 - 3 times per day. Remember to stretch well before running strengthening of foot and calf muscles (eg, heel raises) correct shoes, specifically motion-control shoes and orthotics to correct overpronation. Gradual progression of training programme. Avoid excessive hill training. Incorporate rest into training programme.
 Achilles tendinitis is an irritation/inflammation in the achilles tendon, which attaches to the back of the heel. It is often a result of overuse and occurs frequently in runners who have altered their training suddenly, either with regard to duration or intensity. This injury is also prevalent in middle-aged people who are active.
Achilles tendinitis is an irritation/inflammation in the achilles tendon, which attaches to the back of the heel. It is often a result of overuse and occurs frequently in runners who have altered their training suddenly, either with regard to duration or intensity. This injury is also prevalent in middle-aged people who are active.
Causes
Over-pronation, injury and overstresses of the tendon are some of the most common causes. Risk factors include tight heel cords, poor foot alignment, and recent changes in activities or shoes. During a normal gait cycle, the upper and lower leg rotate in unison (i.e. internally during pronation and externally during supination). However, when a person over-pronates, the lower leg is locked into the foot and therefore continues to rotate internally past the end of the contact phase while the femur begins to rotate externally at the beginning of midstance. The Gastrocnemius muscle is attached to the upper leg and rotates externally while the Soleus muscle is attached to the lower leg and rotates internally during pronation. The resulting counter rotation of the upper and lower leg causes a shearing force to occur in the Achilles tendon. This counter rotation twists the tendon at its weakest area, namely the Achilles tendon itself, and causes the inflammation. Since the tendon is avascular, once inflammation sets in, it tends to be chronic.
Symptoms
People with Achilles tendinitis may experience pain during and after exercising. Running and jumping activities become painful and difficult. Symptoms include stiffness and pain in the back of the ankle when pushing off the ball of the foot. For patients with chronic tendinitis (longer than six weeks), x-rays may reveal calcification (hardening of the tissue) in the tendon. Chronic tendinitis can result in a breakdown of the tendon, or tendinosis, which weakens the tendon and may cause a rupture.
Diagnosis
A doctor examines the patient, checking for pain and swelling along the posterior of the leg. The doctor interviews the patient regarding the onset, history, and description of pain and weakness. The muscles, tissues, bones, and blood vessels may be evaluated with imaging studies, such as X-ray, ultrasound, or MRI.
Nonsurgical Treatment
The initial aim of the treatment in acute cases is to reduce strain on the tendon and reduce inflammation until rehabilitation can begin. This may involve, avoiding or severely limiting activities that may aggravate the condition, such as running or uphill climbs. Using shoe inserts (orthoses) to take pressure off the tendon. Wear supportive shoes. Reducing Inflammation by icing. Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Heel cups and heel lifts can be used temporarily to take pressure off the tendon, but must not be used long term as it can lead to a shortening of the calf. Calf Compression Sleeves. Placing the foot in a cast or restrictive ankle-boot to minimize movement and give the tendon time to heal. This may be recommended in severe cases and used for about eight weeks.

Surgical Treatment
There are three common procedures that doctor preform in order help heal the tendinitis depending on the location of the tendinitis and amount of damage to the tendon, including: Gastrocnemius recession - With this surgery doctors lengthen the calf muscles because the tight muscles increases stress on the Achilles tendon. The procedure is typically done on people who have difficulty flexing their feet even with constant stretching. Debridement and Repair - When there is less than 50% damage in the tendon, it is possible for doctors to remove the injured parts and repair the healthy portions. This surgery is most done for patients who are suffering from bone spurs or arthritis. To repair the tendon doctors may use metal or plastic anchors to help hold the Achilles tendon in place. Patients have to wear a boot or cast for 2 weeks or more, depending and the damage done to the tendon. Debridement with Tendon Transfer - When there is more the 50% damage done to the Achilles tendon, and Achilles tendon transfer is preformed because the remain healthy tissue is not strong enough. The tendon that helps the big toe move is attached to give added strength to the damaged Achilles. After surgery, most patients don?t notice any difference when they walk or run.
Prevention
Stretching of the gastrocnemius (keep knee straight) and soleus (keep knee bent) muscles. Hold each stretch for 30 seconds, relax slowly. Repeat stretches 2 - 3 times per day. Remember to stretch well before running strengthening of foot and calf muscles (eg, heel raises) correct shoes, specifically motion-control shoes and orthotics to correct overpronation. Gradual progression of training programme. Avoid excessive hill training. Incorporate rest into training programme.
Concerning Achilles Tendonitis
Overview
 Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury common in many sports that require lots of running and jumping. Once this condition becomes more chronic adhesions that form along the tissues and the injury becomes more of a tendinosis. Treatment for a tendinosis is much different that for a tendinitis, so it is important to recognize what stage the injury is at in order to treat it appropriately. An acute achilles tendinitis involves inflammation and would be treated with rest, ice, etc. Once the inflammation has decreased, research shows that eccentric exercises are beneficial. Once there is tendinosis, it becomes imperative to break up those adhesions with ART and prescribe appropriate stretches and exercises.
Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury common in many sports that require lots of running and jumping. Once this condition becomes more chronic adhesions that form along the tissues and the injury becomes more of a tendinosis. Treatment for a tendinosis is much different that for a tendinitis, so it is important to recognize what stage the injury is at in order to treat it appropriately. An acute achilles tendinitis involves inflammation and would be treated with rest, ice, etc. Once the inflammation has decreased, research shows that eccentric exercises are beneficial. Once there is tendinosis, it becomes imperative to break up those adhesions with ART and prescribe appropriate stretches and exercises.
Causes
Achilles tendinitis is usually caused by straining the Achilles tendon through intense activity or a sudden increase in exercise. Individuals who play basketball often develop Achilles tendinitis as a result of pivoting, jumping, and running. These repetitive movements put pressure on the tendon and can gradually wear it down over time. Increasing the intensity of your workouts may also lead to the development of Achilles tendinitis. This is commonly seen in long distance runners who do quite a bit of uphill running. Similarly, if you start exercising more frequently you may also develop the condition due to overuse of the tendon. Not stretching properly before exercise can also make the tendon more prone to injury. Achilles tendinitis is also common in individuals whose feet have a flattened arch, as this places more stress on the tendon. The condition can also be triggered by arthritis, as joint pain can cause one to compensate by putting more pressure on the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms
The pain associated with Achilles tendonitis can come on gradually or be caused by some type of leg or foot trauma. The pain can be a shooting, burning, or a dull ache. You can experience the pain at either the insertion point on the back of the heel or upwards on the Achilles tendon within a few inches. Swelling is also common along the area with the pain. The onset of discomfort at the insertion can cause a bump to occur called a Haglund's deformities or Pump bump. This can be inflammation in the bursa sac that surrounds the insertion of the Achilles tendon, scar tissue from continuous tares of the tendon, or even some calcium buildup. In this situation the wearing of closed back shoes could irritate the bump. In the event of a rupture, which is rare, the foot will not be able to go through the final stage of push off causing instability. Finally, you may experience discomfort, even cramping in the calf muscle.
Diagnosis
During an examination of the foot and ankle, you doctor will look for the following signs, Achilles tendon swelling or thickening. Bone spurs appearing at the lower part of the tendon at the back of the hell. Pain at the middle or lower area of the Achilles tendon. Limited range of motion of the foot and ankle, and a decreased ability to flex the foot. Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. X-rays show images of the bones and can help the physician to determine if the Achilles tendon has become hardened, which indicated insertional Achilles tendinitis. MRI scans may not be necessary, but they are important guides if you are recommended to have surgical treatment. An MRI can show the severity of the damage and determine what kind of procedure would be best to address the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment for Achilles tendonitis, depends on the severity of the injury. If heel pain, tenderness, swelling, or discomfort in the back of the lower leg occurs, physical activity that produces the symptoms should be discontinued. If the problem returns or persists, a medical professional should be consulted. If pain develops even with proper stretching and training techniques, the patient should consult a podiatrist to check for hyperpronation and adequate arch support. The addition of an orthotic may be enough to maintain good arch and foot alignment and eliminate pain. If damage to the tendon is minor, the injury may respond to a simple course of treatment known as RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation). Patients are advised to rest the tendon by keeping off their feet as much as possible, apply ice packs for 20 minutes at a time every hour for a day or two to reduce swelling, compress the ankle and foot with a firmly (not tightly) wrapped elastic bandage and elevate the foot whenever possible to minimize swelling. A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as ibuprofen may be used to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery for an acute Achilles tendon tear is seemingly straightforward. The ends of the torn tendon are surgically exposed and sutures are used to tie the ends together. The sutures used to tie together the torn tendon ends are thick and strong, and are woven into the Achilles both above and below the tear. While the concepts of surgery are straightforward, the execution is more complex. Care must be taken to ensure the tendon is repaired with the proper tension -- not too tight or too loose. The skin must be taken care of, as excessive handling of the soft tissues can cause severe problems including infection and skin necrosis. Nerves are located just adjacent to the tendon, and must be protected to prevent nerve injury. If surgery is decided upon, it is usually performed within days or weeks of the injury. The idea is to perform the repair before scar tissue has formed, which would make the repair more difficult. Some surgeons may recommend delaying surgery a few days from the initial injury to allow swelling to subside before proceeding with the repair.
Prevention
If you're just getting started with your training, be sure to stretch after running, and start slowly, increasing your mileage by no more than 10% per week. Strengthen your calf muscles with exercises such as toe raises. Work low-impact cross-training activities, such as cycling and swimming, into your training.
 Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury common in many sports that require lots of running and jumping. Once this condition becomes more chronic adhesions that form along the tissues and the injury becomes more of a tendinosis. Treatment for a tendinosis is much different that for a tendinitis, so it is important to recognize what stage the injury is at in order to treat it appropriately. An acute achilles tendinitis involves inflammation and would be treated with rest, ice, etc. Once the inflammation has decreased, research shows that eccentric exercises are beneficial. Once there is tendinosis, it becomes imperative to break up those adhesions with ART and prescribe appropriate stretches and exercises.
Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury common in many sports that require lots of running and jumping. Once this condition becomes more chronic adhesions that form along the tissues and the injury becomes more of a tendinosis. Treatment for a tendinosis is much different that for a tendinitis, so it is important to recognize what stage the injury is at in order to treat it appropriately. An acute achilles tendinitis involves inflammation and would be treated with rest, ice, etc. Once the inflammation has decreased, research shows that eccentric exercises are beneficial. Once there is tendinosis, it becomes imperative to break up those adhesions with ART and prescribe appropriate stretches and exercises.
Causes
Achilles tendinitis is usually caused by straining the Achilles tendon through intense activity or a sudden increase in exercise. Individuals who play basketball often develop Achilles tendinitis as a result of pivoting, jumping, and running. These repetitive movements put pressure on the tendon and can gradually wear it down over time. Increasing the intensity of your workouts may also lead to the development of Achilles tendinitis. This is commonly seen in long distance runners who do quite a bit of uphill running. Similarly, if you start exercising more frequently you may also develop the condition due to overuse of the tendon. Not stretching properly before exercise can also make the tendon more prone to injury. Achilles tendinitis is also common in individuals whose feet have a flattened arch, as this places more stress on the tendon. The condition can also be triggered by arthritis, as joint pain can cause one to compensate by putting more pressure on the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms
The pain associated with Achilles tendonitis can come on gradually or be caused by some type of leg or foot trauma. The pain can be a shooting, burning, or a dull ache. You can experience the pain at either the insertion point on the back of the heel or upwards on the Achilles tendon within a few inches. Swelling is also common along the area with the pain. The onset of discomfort at the insertion can cause a bump to occur called a Haglund's deformities or Pump bump. This can be inflammation in the bursa sac that surrounds the insertion of the Achilles tendon, scar tissue from continuous tares of the tendon, or even some calcium buildup. In this situation the wearing of closed back shoes could irritate the bump. In the event of a rupture, which is rare, the foot will not be able to go through the final stage of push off causing instability. Finally, you may experience discomfort, even cramping in the calf muscle.
Diagnosis
During an examination of the foot and ankle, you doctor will look for the following signs, Achilles tendon swelling or thickening. Bone spurs appearing at the lower part of the tendon at the back of the hell. Pain at the middle or lower area of the Achilles tendon. Limited range of motion of the foot and ankle, and a decreased ability to flex the foot. Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. X-rays show images of the bones and can help the physician to determine if the Achilles tendon has become hardened, which indicated insertional Achilles tendinitis. MRI scans may not be necessary, but they are important guides if you are recommended to have surgical treatment. An MRI can show the severity of the damage and determine what kind of procedure would be best to address the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Treatment for Achilles tendonitis, depends on the severity of the injury. If heel pain, tenderness, swelling, or discomfort in the back of the lower leg occurs, physical activity that produces the symptoms should be discontinued. If the problem returns or persists, a medical professional should be consulted. If pain develops even with proper stretching and training techniques, the patient should consult a podiatrist to check for hyperpronation and adequate arch support. The addition of an orthotic may be enough to maintain good arch and foot alignment and eliminate pain. If damage to the tendon is minor, the injury may respond to a simple course of treatment known as RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation). Patients are advised to rest the tendon by keeping off their feet as much as possible, apply ice packs for 20 minutes at a time every hour for a day or two to reduce swelling, compress the ankle and foot with a firmly (not tightly) wrapped elastic bandage and elevate the foot whenever possible to minimize swelling. A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as ibuprofen may be used to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery for an acute Achilles tendon tear is seemingly straightforward. The ends of the torn tendon are surgically exposed and sutures are used to tie the ends together. The sutures used to tie together the torn tendon ends are thick and strong, and are woven into the Achilles both above and below the tear. While the concepts of surgery are straightforward, the execution is more complex. Care must be taken to ensure the tendon is repaired with the proper tension -- not too tight or too loose. The skin must be taken care of, as excessive handling of the soft tissues can cause severe problems including infection and skin necrosis. Nerves are located just adjacent to the tendon, and must be protected to prevent nerve injury. If surgery is decided upon, it is usually performed within days or weeks of the injury. The idea is to perform the repair before scar tissue has formed, which would make the repair more difficult. Some surgeons may recommend delaying surgery a few days from the initial injury to allow swelling to subside before proceeding with the repair.
Prevention
If you're just getting started with your training, be sure to stretch after running, and start slowly, increasing your mileage by no more than 10% per week. Strengthen your calf muscles with exercises such as toe raises. Work low-impact cross-training activities, such as cycling and swimming, into your training.
Causes Of Top Of Foot Pain And Treatment Options
Although itching and blistery feet may be a sign of Athlete's foot, those who have constant numbness or tingling in their feet may be suffering from a condition known as peripheral neuropathy. You can barely remember the last time you weren't bothered by foot pain. For most of us foot pain occurs at sometime in our life. Foot complaining of pain, too often? Foot pain around the ankle is quite common.
As soon as the girl's feet were removed from the pan, the bandages were wrapped tightly around the smallest broken toes and pulled securely in and under the heel, till only the large toe was left free. Even though the young girl usually was screaming in agony, her determined mother, aunt(s), and grandmother worked together to forcefully draw together the heel and toe, breaking the arch.
My web site has been designed to offer information about podiatric Foot care We want you to feel comfortable in ouroffice. Dr. Metzl breaks down what "Plantar Fasciitis" is, how to prevent it, and how to cure it. For 5 to 6 minutes perform as many sets of 15 Rows from Plank, 15 Push-ups, and 15 Sit-ups as possible. Dr. Metzl breaks down what "Runner's Knee" is, how to prevent it, and how to cure it. Dr. Metzl breaks down what IT Band Syndrome is, how to prevent it, and how to cure it. Feet and ankles are built tough, capable of sustaining two or three times our body weight. If your foot is too stiff to bear the impact, a tibial stress fracture could result.
Blood glucose levels under control: Meal planning, regular blood glucose monitoring, substantial activity and right diabetes medications including insulin can all go a long way toward relieving the pain associated with the nerve damage. Look them over: Provide your feet a careful going-over every night to make sure that you haven't developed a cut, scrape, sore, blister or any other tiny problem.
I recently stopped wearing them for a few months, and the heel pain returned, so I'm ordering more for my shoes. When I initially put your inserts into my shoes, they felt a bit strange, especially in my arches. Shoes with high heels can create much trouble for your feet.
One study found that 95% of women who used an insert and did simple stretching exercises for the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia experienced improvement after 8 weeks. If these treatments fail, the patient may need prescription heel orthotics and extended physical therapy. Achilles tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendon that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Such people tend to roll their feet too far inward when walking, and may bounce when they walk.
The cause of plantar fasciitis is often unknown. Plantar fasciitis accounts for up to 9% of all running injuries. Other causes of this injury include poorly-fitting shoes, lack of calf flexibility, or an uneven stride that causes an abnormal and stressful impact on the foot. Embarking on an exercise program as soon as possible and using NSAIDs, splints, or heel pads as needed can help relieve the problem. Pain that does not subside with NSAIDs may require more intensive treatments, including leg supports and even surgery. With stretching treatments, the plantar fascia nearly always heals by itself but it may take as long as a year, with pain occurring intermittently. Heel cups are not very useful. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT).
As soon as the girl's feet were removed from the pan, the bandages were wrapped tightly around the smallest broken toes and pulled securely in and under the heel, till only the large toe was left free. Even though the young girl usually was screaming in agony, her determined mother, aunt(s), and grandmother worked together to forcefully draw together the heel and toe, breaking the arch.
My web site has been designed to offer information about podiatric Foot care We want you to feel comfortable in ouroffice. Dr. Metzl breaks down what "Plantar Fasciitis" is, how to prevent it, and how to cure it. For 5 to 6 minutes perform as many sets of 15 Rows from Plank, 15 Push-ups, and 15 Sit-ups as possible. Dr. Metzl breaks down what "Runner's Knee" is, how to prevent it, and how to cure it. Dr. Metzl breaks down what IT Band Syndrome is, how to prevent it, and how to cure it. Feet and ankles are built tough, capable of sustaining two or three times our body weight. If your foot is too stiff to bear the impact, a tibial stress fracture could result.
Blood glucose levels under control: Meal planning, regular blood glucose monitoring, substantial activity and right diabetes medications including insulin can all go a long way toward relieving the pain associated with the nerve damage. Look them over: Provide your feet a careful going-over every night to make sure that you haven't developed a cut, scrape, sore, blister or any other tiny problem.
I recently stopped wearing them for a few months, and the heel pain returned, so I'm ordering more for my shoes. When I initially put your inserts into my shoes, they felt a bit strange, especially in my arches. Shoes with high heels can create much trouble for your feet.

One study found that 95% of women who used an insert and did simple stretching exercises for the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia experienced improvement after 8 weeks. If these treatments fail, the patient may need prescription heel orthotics and extended physical therapy. Achilles tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendon that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Such people tend to roll their feet too far inward when walking, and may bounce when they walk.

The cause of plantar fasciitis is often unknown. Plantar fasciitis accounts for up to 9% of all running injuries. Other causes of this injury include poorly-fitting shoes, lack of calf flexibility, or an uneven stride that causes an abnormal and stressful impact on the foot. Embarking on an exercise program as soon as possible and using NSAIDs, splints, or heel pads as needed can help relieve the problem. Pain that does not subside with NSAIDs may require more intensive treatments, including leg supports and even surgery. With stretching treatments, the plantar fascia nearly always heals by itself but it may take as long as a year, with pain occurring intermittently. Heel cups are not very useful. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT).

Causes Of Top Of Foot Pain And Treatment Options
A foot pain is a common syndrome among the individuals and it can be acute in few cases if left unattended. Psoriatic arthritis can cause pain and swelling beyond the joints. Yes it takes spectacular efforts and extraordinary energy to become a successful athlete. Each foot contains 26 bones, which form two arches.
There are many conservative treatments for plantar fasciitis that when used accordingly are very successful. Your podiatric physician may refer you to a physical therapist to aid in your treatment and to teach you the most effective stretching techniques for your foot type and condition. You may also be advised to wear a night splint that stretches your tendons and fascia in your foot while you sleep. These treatments can significantly reduce the inflammation of your plantar fascia and thus reduce your pain. You should be wearing shoes that properly stabilize your foot and support your arch. Your podiatric physician can provide you with a prefabricated or custom orthotic that would give your achy foot the support it need. It takes time and therapy to improve the integrity of the tissue.
Addressing your foot biomechanics can add yards to your game and make your golf outing much more enjoyable.
During the golf swing the body acts as a whip, power production starts with the feet pushing against the ground. Maintenance of proper foot alignment on the back swing is critical for control of the downswing and contact position. The front heel occasionally comes off the ground to promote a full shoulder turn. Golf should always be played from the insides of the feet.
As you can imagine, healthy feet are critical to a successful golf game.
A podiatrist, is a foot specialist, and goes to school for a lot of years to be able to hold someone's foot in their hands and listen to the type of pain you're suffering from and be able to tell you what the problem is. You should expect your doctor to ask you about the types of shoes you wear and what physical activity you engage in that might have resulted in the foot pain. The x-ray can tell the doctor if there are small breaks, fractures or fissures that could be causing your foot pain. MRI machines (magnetic resonance imaging) can be used in the same way as the x-ray to see inside your foot without having to cut you open. The doctor can then tell if there are any problems with the bones and the soft tissue inside the foot. Mild to Severe Pain: Human foot has 30 joints and 28 bones.
In Case That fair regulating just isn't actually done running NSAIDs because mutual treatments followed by second collection choices with the immunosuppressants such as methotrexate potentially leflunomide would be combined with the treatment ideas. But there are also plenty of other causes that can cause chronic cramps in the feet. Sometimes, the pain is mild, sometimes it is severe.
Unlike the great Roman arches the ones in our feet are designed to be flexible- to "give and take"- upon impact with the ground. That is how the arches both absorb and reflect the force of impact back to the outside world. The arches in our feet are complex structures made up of 24 bones. One of the main sources of foot arch pain is a condition known as plantar fasciitis.
There are also many muscles, tendons and ligaments within your foot. The bones, ligaments and tendons within your foot form the foot arches. These arches are called the longitudinal and transverse arches. It is your foot arches that allow your foot to hold up the weight of your body. Nerves also provide sensation to the skin of your foot. Metatarsalgia is a general name given to pain in the front part of your foot under the heads of your metatarsal bones. The pain can occur in one or both feet.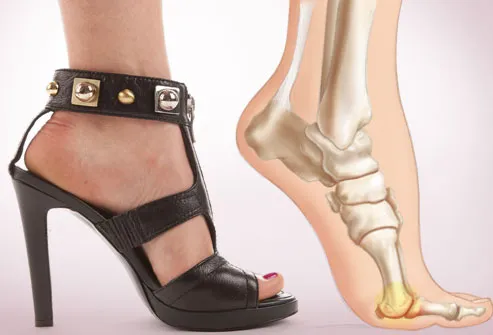
There are many conservative treatments for plantar fasciitis that when used accordingly are very successful. Your podiatric physician may refer you to a physical therapist to aid in your treatment and to teach you the most effective stretching techniques for your foot type and condition. You may also be advised to wear a night splint that stretches your tendons and fascia in your foot while you sleep. These treatments can significantly reduce the inflammation of your plantar fascia and thus reduce your pain. You should be wearing shoes that properly stabilize your foot and support your arch. Your podiatric physician can provide you with a prefabricated or custom orthotic that would give your achy foot the support it need. It takes time and therapy to improve the integrity of the tissue.
Addressing your foot biomechanics can add yards to your game and make your golf outing much more enjoyable.
During the golf swing the body acts as a whip, power production starts with the feet pushing against the ground. Maintenance of proper foot alignment on the back swing is critical for control of the downswing and contact position. The front heel occasionally comes off the ground to promote a full shoulder turn. Golf should always be played from the insides of the feet.
As you can imagine, healthy feet are critical to a successful golf game.
A podiatrist, is a foot specialist, and goes to school for a lot of years to be able to hold someone's foot in their hands and listen to the type of pain you're suffering from and be able to tell you what the problem is. You should expect your doctor to ask you about the types of shoes you wear and what physical activity you engage in that might have resulted in the foot pain. The x-ray can tell the doctor if there are small breaks, fractures or fissures that could be causing your foot pain. MRI machines (magnetic resonance imaging) can be used in the same way as the x-ray to see inside your foot without having to cut you open. The doctor can then tell if there are any problems with the bones and the soft tissue inside the foot. Mild to Severe Pain: Human foot has 30 joints and 28 bones.
In Case That fair regulating just isn't actually done running NSAIDs because mutual treatments followed by second collection choices with the immunosuppressants such as methotrexate potentially leflunomide would be combined with the treatment ideas. But there are also plenty of other causes that can cause chronic cramps in the feet. Sometimes, the pain is mild, sometimes it is severe.

Unlike the great Roman arches the ones in our feet are designed to be flexible- to "give and take"- upon impact with the ground. That is how the arches both absorb and reflect the force of impact back to the outside world. The arches in our feet are complex structures made up of 24 bones. One of the main sources of foot arch pain is a condition known as plantar fasciitis.

There are also many muscles, tendons and ligaments within your foot. The bones, ligaments and tendons within your foot form the foot arches. These arches are called the longitudinal and transverse arches. It is your foot arches that allow your foot to hold up the weight of your body. Nerves also provide sensation to the skin of your foot. Metatarsalgia is a general name given to pain in the front part of your foot under the heads of your metatarsal bones. The pain can occur in one or both feet.
